Listeria
Listeria is a gram-positive rod-shaped bacterium that can grow under either anaerobic (without oxygen) or aerobic (with oxygen) conditions. Of the six species of Listeria, only L. monocytogenes causes disease in humans. These bacteria multiply best at 30-37oC, but also multiply better than all other bacteria at refrigerator temperatures, something that allows temperature to be used as a means of differentiating Listeria from other contaminating bacteria.
Called an “opportunistic pathogen", Listeria is noted to cause many cases per year of severe invasive illness. Perhaps not surprisingly then, "foodborne illness caused" by Listeria monocytogenes has raised significant public health concern in the United States, Europe, and other areas of the world.
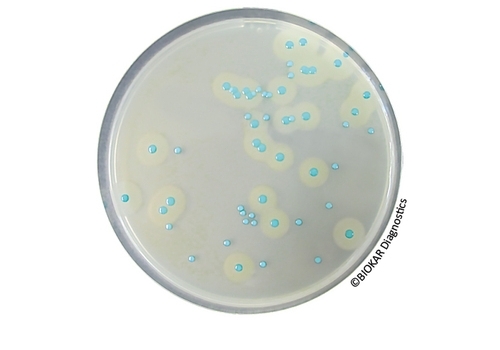
COMPASS® Listeria Agar
COMPASS® Listeria Agar COMPASS® Listeria constitutes a method constitutes a method for the..
More
CONFIRM’ L.mono Agar®
CONFIRM’ L. mono Agar® CONFIRM’ L. mono Agar® is a solid culture media designed for the..
More
CONFIRM’ L.mono Broth
CONFIRM’ L. mono broth® The CONFIRM’ L. mono broth® is a liquid media destined for the..
More
Fraser Broth
Fraser Broth Fraser broth is used for the selective secondary enrichment of Listeria..
More
Half-Fraser Broth
Half Fraser Broth Half Fraser broth is used for the selective and differential (primary..
More
Lısteria Enrıchment Broth
Lısteria Enrıchment Broth (MODIFIED UVM I) The enrichment broths UVM (University of Vermont)..
More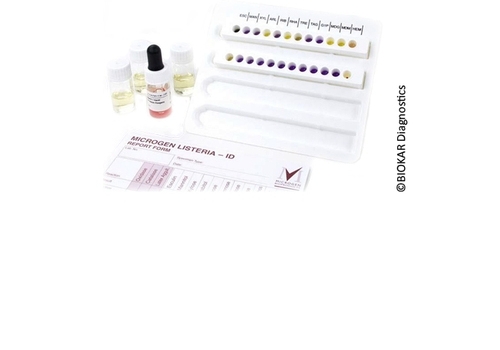
Microgen Listeria-ID system
Microgen Listeria-ID system The Microgen Listeria-ID system allows the identification of six..
More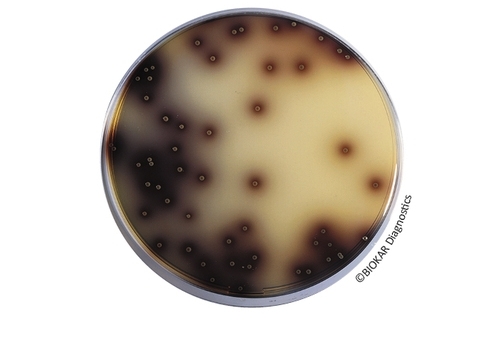
Oxford Agar
Oxford Agar Oxford Agar is a selective medium used for the differentiation, the isolation and..
More
Palcam Agar
Palcam Agar PALCAM Agar is a selective medium used for the differentiation and isolation of..
More
TSYE Agar
TSYE Agar TSYE agar is a universal medium used in a number of applications or protocols. Given..
More